Basic differences among working stress and limit state method
- Concrete Cost Estimator
- Concrete Continuous Footing
- Landscape Bidding and Estimating
- Construction Cost Estimating
- Concrete and steel cost estimation
- Construction Cost Estimate Breakdown
- Construction Estimating Worksheet
- Home Construction Cost Estimate
- Estimate Pricing Sheet
- Sheet for General Contractor
- Construction Cost Estimate
- Labor Materials Cost Estimator
- Masonry Estimating Sheet
- Sheet for Building Contractor
- Construction Schedule Bar chart
- General Cost Estimator Sheet
- General Construction Estimate
- Building and Road Estimating Sheet
- Detailed expense estimates
- Door and Window Takeoff Sheet
- General Construction Cost Estimating Sheet

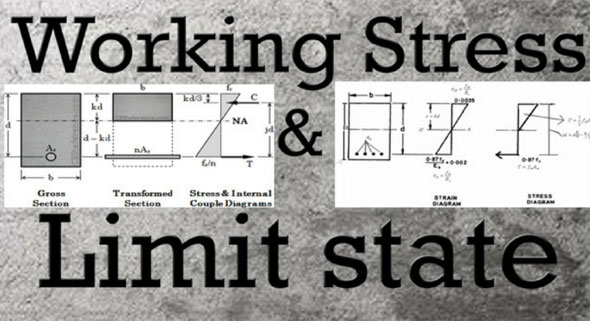
WORKING STRESS METHOD: It's a conventional method that is effective for reinforced concrete design where concrete is supposed to be elastic. Steel and concrete function together elastically where the connection among loads and stresses is linear.
Limit state design (LSD) alias load and resistance factor design (LRFD), stands for a design method that is employed in structural engineering. A limit state is a condition of a structure across which it no more meets the applicable design criteria.
Given below, the points of differences among working stress method and limit state method.
This method is created on the basis of the elastic theory that suspects that concrete and steel are elastic and the stress strain curve is linear for both.
This method is developed on the basis of the actual stress-strain curves of steel and concrete. For concrete, the stress strain curve is nonlinear.
In this method the factor of safety are employed to the yield stresses to obtain permissible stresses.
In this method, Partial safety factors are employed to obtain the design values of stresses.
No factor of safety is applied for loads.
Design loads are obtained by multiplying partial safety factors of load to the working loads.
Proper margin of safety is unidentified.
Proper margin of safety is recognized.
This method provides deeper sections, so it is not cost-effective.
This method is cost-effective because it provides thinner sections.
This method supposes that the actual loads, allowable stresses and factors of safety are recognized. So it is known as deterministic method.
This method is developed on the basis of the probabilistic approach which depends upon the actual data or experience, hence it is known as non-deterministic method.
- Application of concrete calculator
- Roofing Calculator can streamline the roof estimating process
- House construction cost calculator
- Engineering column design excel spreadsheet
- Material Estimating Sheet with Excel
- Materials List and Cost Estimate Worksheet
- Concrete Slab Estimating Calculator Sheet
- Common types of foundations for buildings
- Online calculation of construction materials
- Estimating with Excel for the Small Contractor
- Concrete Beam Design Spreadsheet
- Virtual Construction Management app for construction
- Autodesk’s Project Skyscraper
- Reed Construction’s Reed Insight
- Manage your construction project documentation
- Costimator, the popular cost estimating software
- On Center Software for construction professionals
- Free Construction Estimating Software
- Plumbing Calc Pro
- Cost Estimate Worksheet
- HVAC Piping Quantity Takeoff Worksheet
- Construction Estimating Software Sheet
- Estimate Cost Templates
- Construction Punch List
- Construction cost estimating template consisting estimating basic
- Gantt Chart Template for Excel
- Download Civil Engineering Spreadsheets with Verification
- The Building Advisor Estimating and Budgeting Worksheet
- Spreadsheet for design of concrete bridge
- Construction Estimating Software Free








