Brief overview of Reinforcement Concrete
- Concrete Cost Estimator
- Concrete Continuous Footing
- Landscape Bidding and Estimating
- Construction Cost Estimating
- Concrete and steel cost estimation
- Construction Cost Estimate Breakdown
- Construction Estimating Worksheet
- Home Construction Cost Estimate
- Estimate Pricing Sheet
- Sheet for General Contractor
- Construction Cost Estimate
- Labor Materials Cost Estimator
- Masonry Estimating Sheet
- Sheet for Building Contractor
- Construction Schedule Bar chart
- General Cost Estimator Sheet
- General Construction Estimate
- Building and Road Estimating Sheet
- Detailed expense estimates
- Door and Window Takeoff Sheet
- General Construction Cost Estimating Sheet

This is a great instructional video for construction professionals. The video briefly describes the reinforcement concrete process.
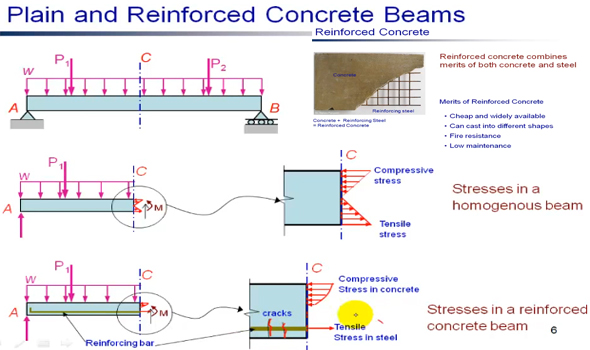
Reinforced concrete (RC) stands for a composite material where concrete's comparatively small tensile strength and ductility are defied by the addition of reinforcement that contains greater tensile strength or ductility. The reinforcement is generally, though not essentially, steel reinforcing bars (rebar) and is typically implanted inertly in the concrete prior to concrete is arranged.
Reinforcing schemes are usually planned to withstand tensile stresses in specific areas of the concrete that may lead to undesirable cracking and/or structural failure. Modern reinforced concrete includes diversified reinforcing materials which are developed with steel, polymers or alternate composite material in combination with rebar or not. Reinforced concrete is also stressed (in compression) perpetually, in order to make the behaviour of the final structure more improved under working loads. Generally, it is called as pre-tensioning and post-tensioning.
For a solid, ductile and long-lasting construction the reinforcement should contain the following properties:
1. High relative strength
2. High toleration of tensile strain
3. Strong bond to the concrete, regardless of pH, moisture, and similar factors
4. Thermal compatibility, not producing intolerable stresses in response to modifying temperatures.
5. Strength in the concrete environment, regardless of corrosion or sustained stress for example.
- Application of concrete calculator
- Roofing Calculator can streamline the roof estimating process
- House construction cost calculator
- Engineering column design excel spreadsheet
- Material Estimating Sheet with Excel
- Materials List and Cost Estimate Worksheet
- Concrete Slab Estimating Calculator Sheet
- Common types of foundations for buildings
- Online calculation of construction materials
- Estimating with Excel for the Small Contractor
- Concrete Beam Design Spreadsheet
- Virtual Construction Management app for construction
- Autodesk’s Project Skyscraper
- Reed Construction’s Reed Insight
- Manage your construction project documentation
- Costimator, the popular cost estimating software
- On Center Software for construction professionals
- Free Construction Estimating Software
- Plumbing Calc Pro
- Cost Estimate Worksheet
- HVAC Piping Quantity Takeoff Worksheet
- Construction Estimating Software Sheet
- Estimate Cost Templates
- Construction Punch List
- Construction cost estimating template consisting estimating basic
- Gantt Chart Template for Excel
- Download Civil Engineering Spreadsheets with Verification
- The Building Advisor Estimating and Budgeting Worksheet
- Spreadsheet for design of concrete bridge
- Construction Estimating Software Free








