Foundation Design Details
- Concrete Cost Estimator
- Concrete Continuous Footing
- Landscape Bidding and Estimating
- Construction Cost Estimating
- Concrete and steel cost estimation
- Construction Cost Estimate Breakdown
- Construction Estimating Worksheet
- Home Construction Cost Estimate
- Estimate Pricing Sheet
- Sheet for General Contractor
- Construction Cost Estimate
- Labor Materials Cost Estimator
- Masonry Estimating Sheet
- Sheet for Building Contractor
- Construction Schedule Bar chart
- General Cost Estimator Sheet
- General Construction Estimate
- Building and Road Estimating Sheet
- Detailed expense estimates
- Door and Window Takeoff Sheet
- General Construction Cost Estimating Sheet

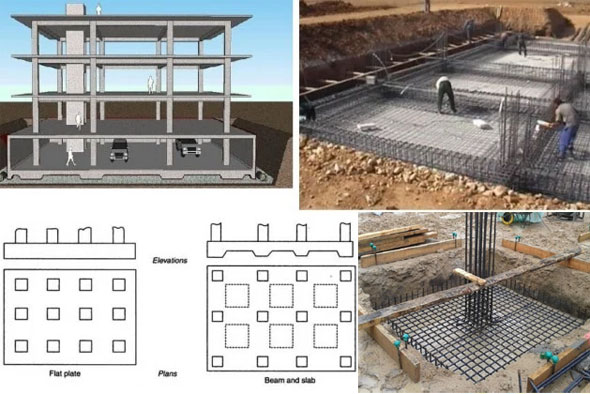
Foundation design allows us to make a proper construction plan for a building foundation. It belongs to an extremely specialized function that is executed by a structural engineer.
The foundation forms the structural base that rests on the ground and provides support to the remaining part of the building. To make perfect foundation design, there should be thorough knowledge on the ground underneath the foundation along with the design and materials provided on the foundation itself.
Depth of the Foundation
Several types of building foundations are available. Normally, the foundations are installed at different depths excluding slab-on-grade foundations, which are provided at ground level. The desired depth of any foundation is influenced by the following factors :
Soil bearing strength: It establishes extent load (weight or force) the subsisting soil can resist.
Soil type: Various types of soil contain diverse properties that can change their applicability for providing support to a foundation.
Frost depth: The frost depth alias frost line means the depth to which the soil freezes in the coldest time of the year. It is mainly utilized to find out the least depth for various types of foundations.
Groundwater table: A high groundwater table restricts the foundation depth along with the type of foundation to be utilized. Groundwater height is normally contained in a soil study.
Minimum depth: The least depth of a foundation normally should not be lower than 18 inches to facilitate extracting the topsoil and variations in ground level.
Foundation Materials
Usually, the foundations are constructed with masonry, like concrete block or brick, or with poured concrete. Masonry materials contain high compressive strength and have strong resistance strength to get rid of the damage caused by moisture and soil as compared to wood and metal materials.
Also Read: How to use BarBeQue software for Reinforcement Bar Bending Schedules for RCC Work
A masonry foundation usually expands over the ground to keep other building materials safe from moisture and other damaging effects of ground contact. Normally, the metal rebar or other materials are used to reinforce the masonry foundations internally. Contractors frequently utilize hydraulic cement to block the pipes or raceways that infiltrate the masonry or concrete foundation.
Some building foundations are constructed with treated wood posts or piers. Under this situation, the foundation supports are pushed deep into the earth and/or stand on a rock or concrete pads. Posts and piers are frequently utilized while building on or near water or where the land is subject to flooding.
One of the very crucial foundation materials is the base, or subbase, which are made of inorganic material provided directly under the foundation. Normally, submerged soil and clay contain limited bearing strength and fail to manage the loads enforced by a building.
So, the soils are excavated and substituted with a dry and uniform dense material like gravel or crushed stone that has greater shear resistance and bearing strength. Base materials also facilitate discharging subsurface water and do not extend with high levels of moisture, similar to soil.
Transmission of Foundation Load
Foundations should be designed in such a manner in order that the loads enforced by the building are transmitted equally to the contact surface to pass the sum of the dead load, live load, and wind load to the ground. The net loading strength that directs to the soil should not surpass the bearing strength of the soil.
Foundation design should also consider the intended settling from the building to make sure that all movement is restrained and uniform to get rid of the damage to the structure. Besides, the overall design of the foundation, superstructure, and characteristics of the ground should be thoroughly checked to recognize the possible useful construction strategies.
- Application of concrete calculator
- Roofing Calculator can streamline the roof estimating process
- House construction cost calculator
- Engineering column design excel spreadsheet
- Material Estimating Sheet with Excel
- Materials List and Cost Estimate Worksheet
- Concrete Slab Estimating Calculator Sheet
- Common types of foundations for buildings
- Online calculation of construction materials
- Estimating with Excel for the Small Contractor
- Concrete Beam Design Spreadsheet
- Virtual Construction Management app for construction
- Autodesk’s Project Skyscraper
- Reed Construction’s Reed Insight
- Manage your construction project documentation
- Costimator, the popular cost estimating software
- On Center Software for construction professionals
- Free Construction Estimating Software
- Plumbing Calc Pro
- Cost Estimate Worksheet
- HVAC Piping Quantity Takeoff Worksheet
- Construction Estimating Software Sheet
- Estimate Cost Templates
- Construction Punch List
- Construction cost estimating template consisting estimating basic
- Gantt Chart Template for Excel
- Download Civil Engineering Spreadsheets with Verification
- The Building Advisor Estimating and Budgeting Worksheet
- Spreadsheet for design of concrete bridge
- Construction Estimating Software Free








