Levelling Problems in Surveying
- Concrete Cost Estimator
- Concrete Continuous Footing
- Landscape Bidding and Estimating
- Construction Cost Estimating
- Concrete and steel cost estimation
- Construction Cost Estimate Breakdown
- Construction Estimating Worksheet
- Home Construction Cost Estimate
- Estimate Pricing Sheet
- Sheet for General Contractor
- Construction Cost Estimate
- Labor Materials Cost Estimator
- Masonry Estimating Sheet
- Sheet for Building Contractor
- Construction Schedule Bar chart
- General Cost Estimator Sheet
- General Construction Estimate
- Building and Road Estimating Sheet
- Detailed expense estimates
- Door and Window Takeoff Sheet
- General Construction Cost Estimating Sheet

Given below common types of errors in leveling:- 1. Instrumental Errors, 2. Collimation Error, 3. Error due to Curvature & Refraction, 4. Other Errors
1. Instrumental error and Correction:
a. Collimation error - Correction: Verify prior to apply and make equal sights.
b. Under sensitive bubble.
c. Errors in staff graduation - Correction: Check
d. Loose tripod head.
e. Telescope not identical to bubble tube - Correction: Permanent adjustment.
f. Telescope not at right angles to the vertical axis - Correction: Permanent adjustment
2. Error of Collimation: Collimation error is found if the collimation axis is not perfectly horizontal while the instrument is level.
3. Curvature & Refraction
Curvature of the earth: The earth seems to “fall away” with distance. The curved shape of the earth signifies that the level surface through the telescope will go away from the horizontal plane via the telescope when the line of sight moves forward to the horizon.
This effect transforms real level rod readings too large by:
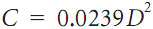
Here D means the sight distance in thousands of feet.
Given below the impacts of curvature:
• Rod reading is very high
• Error is raised proportionally with distance
Also Read: Definition of leveling and some vital terms used in surveying & leveling
Atmospheric Refraction - Refraction mainly belongs to a function of atmospheric pressure and temperature gradients, which lead to the following:
The bending to be up or down by exceptionally variable amounts.
The following three types of temperature gradient (dT/dh) are found:
1. Absorption: It primarily happens at night when the colder ground sop ups heat from the atmosphere.
a. Due to this the atmospheric temperature is raised with distance from the ground and dT/dh > 0.
2. Emission: It primarily happens throughout the day if the warmer ground releases heat into the atmosphere that leads to a negative temperature gradient, i.e. dT/dh < 0.
3. Equilibrium: There is no heat transfer (dT/dh = 0) and happens only in the evening and morning.
4. The result of dT/dh < 0 is to make the light ray to be convex to the ground instead of concave as normally found.
a. This effect raises the closer to the ground the light ray gets and errors in the region of 5 mm/km have caused.
The atmosphere deflects the horizontal line of sight downward, transforming the level rod reading smaller. The usual effect of refraction is identical about 14% of the effect of earth curvature.
Combined Effect of Curvature and Refraction in Survey: The combined effect of curvature and refraction is roughly
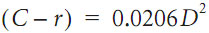
The combined effect of curvature and refraction is calculated with the following formula : C + R = 0.021K2
Here C denotes correction for curvature
R denotes correction for refraction
K denotes sighting distance in thousands of feet
Correlations for various distances
Distance - Correction
100′ - 0.00021′
200′- 0.00082′
500′ - 0.0052′
700′ -0.01′
1 mile - 0.574′
How to eliminate error owing to Curvature and Refraction
1. Exact field methods (choosing shorter shots and balancing shots) can almost minimize errors
2. If possible, staff readings should be retained minimum 0.5 m over the ground,
3. With the use of short observation distances (25 m) leveled for backsight and foresight
4. Air beneath is denser as compared air above, Line of sight is bent downward that nullifies earth curvature error by 14%.
5. Instantaneous Reciprocal Trigonometrical Heightening
6. Observations created at each station at exactly the same time, revokes the effects of curvature and refraction
Other types of errors in leveling:
Type of Error |
Correction |
1. Setting-up of instrument correctly |
|
2. Movement of staff from position while altering level station. |
• Training the staff men |
3. Staff not held vertically. |
• Hold rod tightly; apply head/body to support it. |
4. Parallax: Instrument knocked or moved during backsight-foresight reading |
• change parallax error if any |
5. Ground heating leads to chaotic refraction of light |
• Shorten the length of shots |
6. Tripod or rod settles among measurements e.g Bubble off center |
• Quick measurements among rods |

- Application of concrete calculator
- Roofing Calculator can streamline the roof estimating process
- House construction cost calculator
- Engineering column design excel spreadsheet
- Material Estimating Sheet with Excel
- Materials List and Cost Estimate Worksheet
- Concrete Slab Estimating Calculator Sheet
- Common types of foundations for buildings
- Online calculation of construction materials
- Estimating with Excel for the Small Contractor
- Concrete Beam Design Spreadsheet
- Virtual Construction Management app for construction
- Autodesk’s Project Skyscraper
- Reed Construction’s Reed Insight
- Manage your construction project documentation
- Costimator, the popular cost estimating software
- On Center Software for construction professionals
- Free Construction Estimating Software
- Plumbing Calc Pro
- Cost Estimate Worksheet
- HVAC Piping Quantity Takeoff Worksheet
- Construction Estimating Software Sheet
- Estimate Cost Templates
- Construction Punch List
- Construction cost estimating template consisting estimating basic
- Gantt Chart Template for Excel
- Download Civil Engineering Spreadsheets with Verification
- The Building Advisor Estimating and Budgeting Worksheet
- Spreadsheet for design of concrete bridge
- Construction Estimating Software Free








